
A nap should be 10 to 20 minutes long to get the most restorative benefits. There are different types of naps, but a quick daytime rest should be relatively short. Naps of 30 minutes or longer may leave you feeling less alert, though this varies with age. A 90 minute nap may also be beneficial for many people.
Difference between a nap vs sleep
The difference between sleep and a nap is duration. Naps are typically short, designed to quickly reenergise, whereas sleep lasts for several hours.
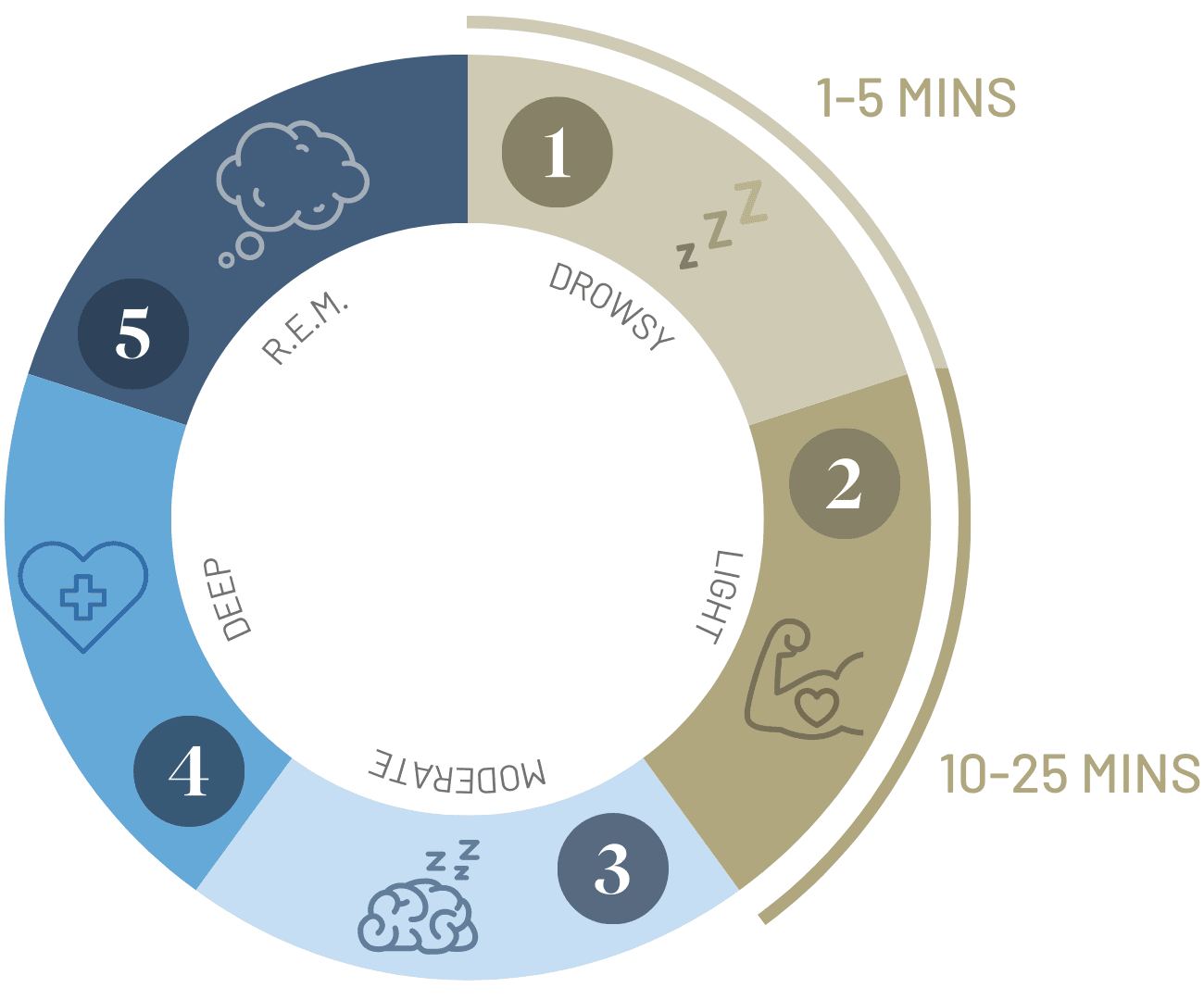
As you rest, your body and brain experience progressively deeper stages of sleep. During the night, you experience these stages in cycles, usually moving between moderate, deep and REM sleep.
The stages of a sleep cycle are:
- Drowsiness and light sleep, where the heartbeat slows and your muscles begin to relax; this is the ideal stage to nap
- Moderate sleep, where you experience brain sleep spindles and a drop in body temperature
- Deep sleep repairs tissues and strengthens the immune system
- R.E.M. (rapid eye movement) is when dreams and nightmares occur
As you rest, your body and brain experience progressively deeper stages of sleep. During the night, we experience these stages in cycles, usually moving between moderate, deep and REM sleep.

The stages of a sleep cycle are:
- Drowsiness and light sleep, where the heartbeat slows and your muscles begin to relax; this is the ideal stage to nap
- Moderate sleep, where you experience brain sleep spindles and a drop in body temperature
- Deep sleep repairs tissues and strengthens the immune system
- R.E.M. (rapid eye movement) is when dreams and nightmares occur
10-25 minute 'power' naps
The purpose of a nap is usually to combat daytime sleepiness or to boost energy. Consequently, you should avoid napping for more than 20-25 minutes, otherwise your body will enter a deeper state of sleep. Deep sleep and REM sleep are harder to wake from, and interrupting these stages leads to sleep inertia. This sensation is characterised by grogginess, brain fog, impaired coordination and temporary confusion. Sleep inertia can be quite dangerous if you need to perform certain high-risk activities or operate machinery immediately afterwards.
longer 90 minute naps
Waking from a brief, light sleep will lessen the likelihood or the effects of sleep inertia. If you feel a 20 minute power nap isn’t quite enough time, try aiming for a 90 minute rest, instead. This duration will ensure that you perform a full sleep cycle, moving through deep and REM sleep and arriving back at a moderate stage. Doing so helps to prevent sleep inertia, as you are not interrupting your deepest sleep, and for some people it may result in more rejuvenation than a brief nap.

Kids vs adults
Children and teenagers need more sleep than adults. Younger children, especially, should be napping throughout the day to meet their needs, depending on their age and routine.
They will gradually reduce the amount of time they need for naps; some may even stop feeling the need for daytime sleep altogether. Teenagers should also be encouraged to take naps when they are able to, if they are feeling tired or deprived of sufficient rest.
Benefits and side effects of napping
Benefits
There are numerous benefits of napping as an adult beyond simply catching up on rest. A nap may help you to:
- Reduce fatigue and sleepiness
- Improve alertness, concentration and performance
- Boost your mood or regulate emotions
- Improve your memory

side effects
Some people find that naps are not ideal for their health or lifestyle. Taking a nap late in the afternoon interferes with the quality of your sleep at night. This is also the case for overly long naps — they can interrupt nighttime sleep patterns if taken consistently.
If you feel a strong urge to nap everyday, it may be an indication of an underlying sleep disorder. A nap should not be a substitute for adequate seep at night.
Finally, though not conclusive, some studies have raised concerns about the long-term effects of napping. They claim that individuals who have frequent, lengthy naps have a higher likelihood of experiencing conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes or depression.
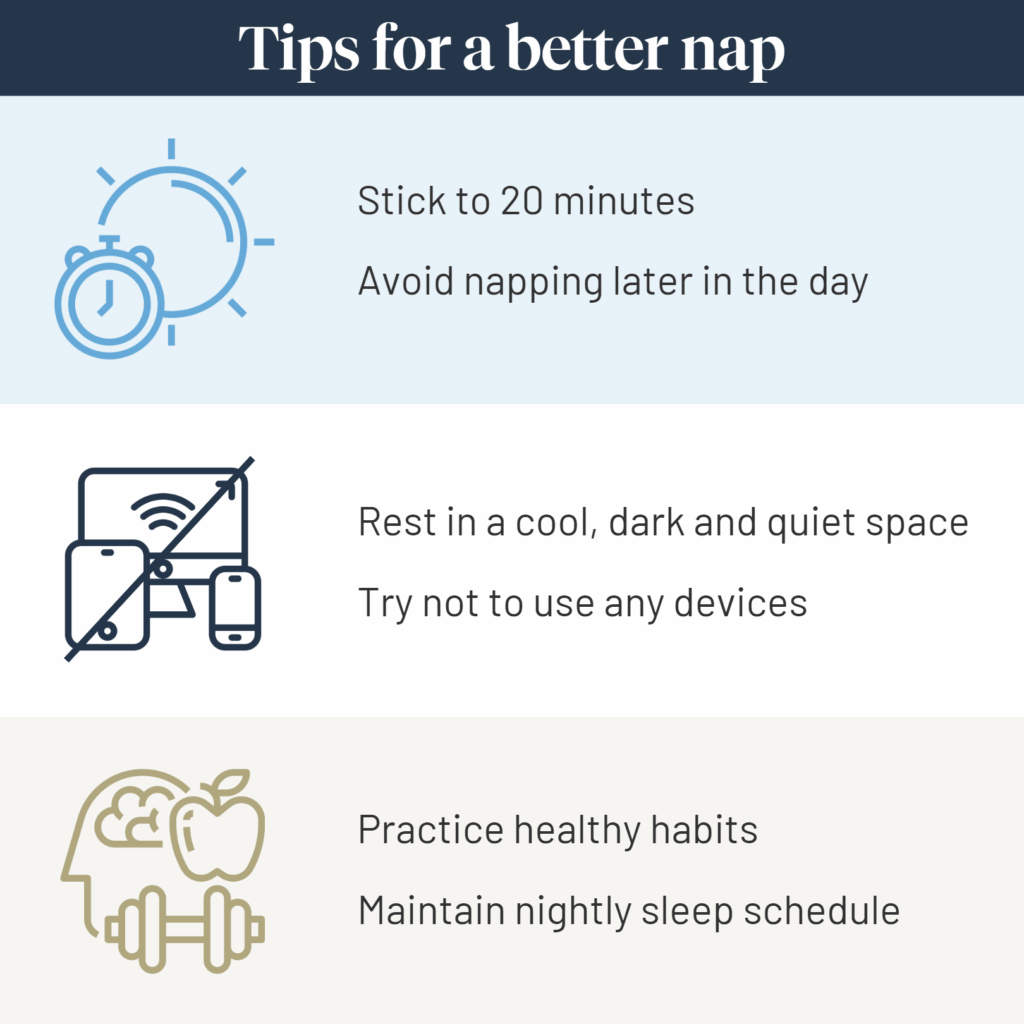
3 tips for napping during the day
1. Aim for the ideal time and duration
We know that it is better to limit your nap to around 20 minutes, but you should also be mindful of the time of day. Napping too late in the afternoon is likely to interfere with your sleep at night, especially if you do so consistently.
Aim to nap around 2pm in the afternoon, or roughly 8 hours before your normal bedtime. You might find it better to nap around lunchtime when we are naturally sleepy.
2. Establish the right environment
Though a typical nap is quite short, it is important to make sure your environment is conducive to sleep. Ensure your space is cool, dark and quiet. Many people find that an uncluttered space helps them to sleep peacefully, as well.
Be aware that napping in your bed is not always ideal. By doing so, you are far more likely to oversleep past the recommended 20-minute limit. So long as it is sufficiently supportive and comfortable, choose a chair, lounge or guest bed instead.
You should also avoid using any electronic devices while trying to nap, except for setting a quick alarm. The light and mental stimulation of prolonged use may inhibit your ability to fall asleep.
3. Consider health factors
It is important not to substitute regular sleep with daytime naps. You still need sufficient rest at night, which is generally 7-9 hours for most adults. If you find that you are napping to catch up on consistently missed sleep, you may need to adjust your schedule or speak with a healthcare professional. In some cases, constant napping is an indicator of an underlying sleep disorder or health condition.
It may also help to practice healthy habits. Research shows that keeping an exercise routine can help to strengthen your circadian rhythms and overall quality of sleep. Rich foods, alcohol or stimulants may make it difficult to fall asleep and nap effectively.

Napping FAQs
Is a 45-minute nap good?
A 45-minute nap is not ideal. After 20 minutes, your body enters deeper sleep. Waking in the middle of this stage leads to sleep inertia or increased grogginess. You may struggle to wake up, and are likely to feel more tired after a 45-minute nap.
Is a 1-hour nap too long?
A 1-hour nap is too long. After 20 minutes, your body enters deeper sleep. Waking in the middle of this stage leads to sleep inertia. If you need more sleep, aim for 90 minutes (or 1.5 hours). You will pass through deep sleep and avoid the worst of the grogginess.
Is a 2-hour nap too long?
A 2 hour nap is typically too long. It may leave you feeling groggy, and could disrupt your nightly sleep cycle. The ideal nap length is 20 minutes, or 90 minutes if you need a bit longer.
How long is considered as nap?
A nap is ideally 10-20 minutes long, or up to 90 minutes in some cases. Sleeping for longer than this timeframe is likely to disturb your normal sleep schedule.

